Create simple Blockchain using Python
- General
Create simple Blockchain using Python
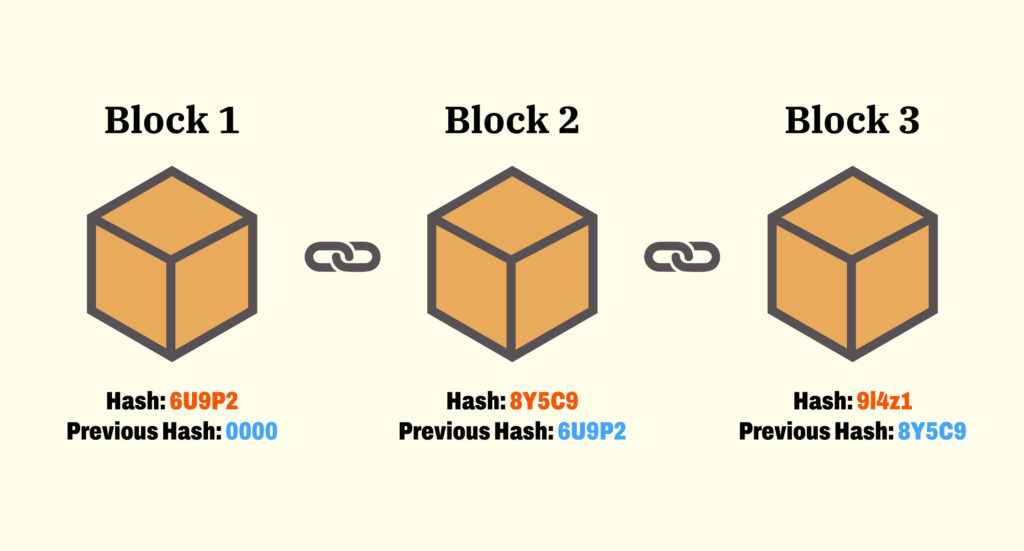
Blockchain is a time-stamped decentralized series of fixed records that contains data of any size is controlled by a large network of computers that are scattered around the globe and not owned by a single organization. Every block is secured and connected with each other using hashing technology which protects it from being tampered by an unauthorized person.
Creating Blockchain using Python, mining new blocks, and displaying the whole blockchain:
- The data will be stored in JSON format which is very easy to implement and easy to read. The data is stored in a block and the block contains multiple data. Each and every minute multiple blocks are added and to differentiate one from the other we will use fingerprinting.
- The fingerprinting is done by using hash and to be particular we will use the SHA256 hashing algorithm. Every block will contain its own hash and also the hash of the previous function so that it cannot get tampered with.
- This fingerprinting will be used to chain the blocks together. Every block will be attached to the previous block having its hash and to the next block by giving its hash.
- The mining of the new block is done by giving successfully finding the answer to the proof of work. To make mining hard the proof of work must be hard enough to get exploited.
- After mining the block successfully the block will then be added to the chain.
- After mining several blocks the validity of the chain must be checked in order to prevent any kind of tampering with the blockchain.
- Then the web app will be made by using Flask and deployed locally or publicly as per the need of the user.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 |
# Python program to create Blockchain # For timestamp import datetime # Calculating the hash # in order to add digital # fingerprints to the blocks import hashlib # To store data # in our blockchain import JSON # Flask is for creating the web # app and jsonify is for # displaying the blockchain from flask import Flask, jsonify class Blockchain: # This function is created # to create the very first # block and set its hash to "0" def __init__(self): self.chain = [] self.create_block(proof=1, previous_hash='0') # This function is created # to add further blocks # into the chain def create_block(self, proof, previous_hash): block = {'index': len(self.chain) + 1, 'timestamp': str(datetime.datetime.now()), 'proof': proof, 'previous_hash': previous_hash} self.chain.append(block) return block # This function is created # to display the previous block def print_previous_block(self): return self.chain[-1] # This is the function for proof of work # and used to successfully mine the block def proof_of_work(self, previous_proof): new_proof = 1 check_proof = False while check_proof is False: hash_operation = hashlib.sha256( str(new_proof**2 - previous_proof**2).encode()).hexdigest() if hash_operation[:5] == '00000': check_proof = True else: new_proof += 1 return new_proof def hash(self, block): encoded_block = json.dumps(block, sort_keys=True).encode() return hashlib.sha256(encoded_block).hexdigest() def chain_valid(self, chain): previous_block = chain[0] block_index = 1 while block_index < len(chain): block = chain[block_index] if block['previous_hash'] != self.hash(previous_block): return False previous_proof = previous_block['proof'] proof = block['proof'] hash_operation = hashlib.sha256( str(proof**2 - previous_proof**2).encode()).hexdigest() if hash_operation[:5] != '00000': return False previous_block = block block_index += 1 return True # Creating the Web # App using flask app = Flask(__name__) # Create the object # of the class blockchain blockchain = Blockchain() # Mining a new block @app.route('/mine_block', methods=['GET']) def mine_block(): previous_block = blockchain.print_previous_block() previous_proof = previous_block['proof'] proof = blockchain.proof_of_work(previous_proof) previous_hash = blockchain.hash(previous_block) block = blockchain.create_block(proof, previous_hash) response = {'message': 'A block is MINED', 'index': block['index'], 'timestamp': block['timestamp'], 'proof': block['proof'], 'previous_hash': block['previous_hash']} return jsonify(response), 200 # Display blockchain in json format @app.route('/get_chain', methods=['GET']) def display_chain(): response = {'chain': blockchain.chain, 'length': len(blockchain.chain)} return jsonify(response), 200 # Check validity of blockchain @app.route('/valid', methods=['GET']) def valid(): valid = blockchain.chain_valid(blockchain.chain) if valid: response = {'message': 'The Blockchain is valid.'} else: response = {'message': 'The Blockchain is not valid.'} return jsonify(response), 200 # Run the flask server locally app.run(host='127.0.0.1', port=5000) |
Output (mine_block):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
{ "index":2, "message":"A block is MINED", "previous_hash":"2d83a826f87415edb31b7e12b35949b9dbf702aee7e383cbab119456847b957c", "proof":533, "timestamp":"2020-06-01 22:47:59.309000" } |
Output (get_chain):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
{ "chain":[{"index":1, "previous_hash":"0", "proof":1, "timestamp":"2020-06-01 22:47:05.915000"},{"index":2, "previous_hash":"2d83a826f87415edb31b7e12b35949b9dbf702aee7e383cbab119456847b957c", "proof":533, "timestamp":"2020-06-01 22:47:59.309000"}], "length":2 } |
Output(valid):
|
1 |
{"message":"The Blockchain is valid."} |
Related content
Auriga: Leveling Up for Enterprise Growth!
Auriga’s journey began in 2010 crafting products for India’s
