A Guide for Latest Library React Navigation 5
- Mobile
A Guide for Latest Library React Navigation 5
For navigation between screens we use this navigation library for react native apps. The stable version of this library React Navigation 5.0, was released in February 2020.
Points we will be covering in this guide –
- Key features of React Navigation 5.0
- Installation and Setup
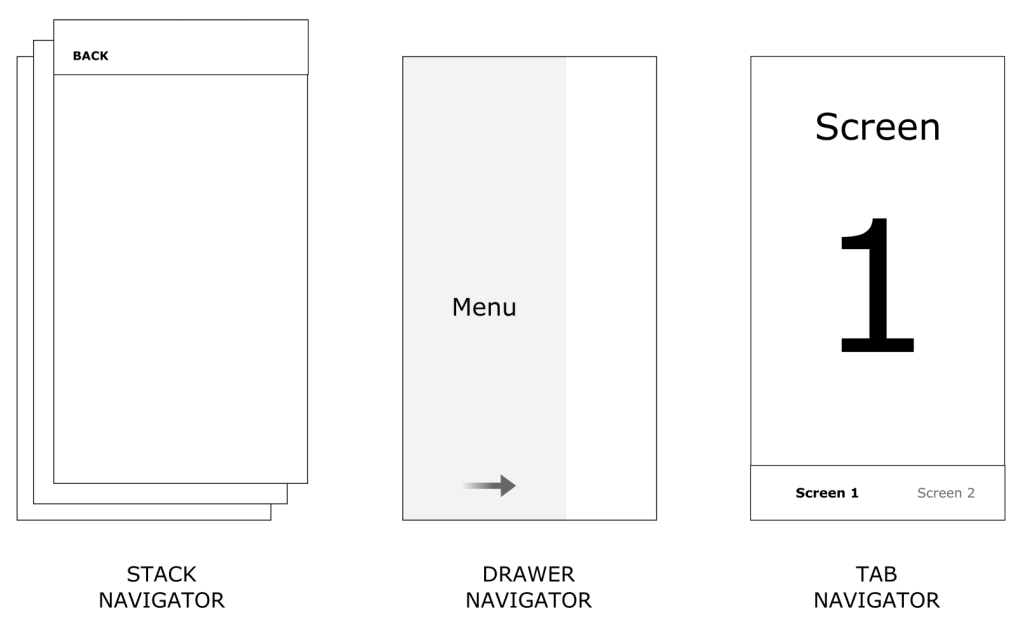
- Stack, Tab and Drawer Navigator
- An example in which all navigators are combined
An Introduction to React Navigation
As we know that mobile apps are made up of different screens, and these screens need to be shown in a particular sequence for various properties. So a basic structure is required to decide this sequence, which we provide in apps using navigators like stack, tab and drawer. React navigation library enables us in implementing navigation in react native apps.
What’s New ? Key features
- Dynamic navigator configuration with component
- New hooks – useNavigation, useRoute, useNavigationState, useFocusEffect, useIsFocused, useLinking, useScrollToTop
- Configuring screen navigation options more intuitive with setOptions, an replacement of static navigationOption
- Easier customization with new theming API
- First-class autocompletion and type-checking with TypeScript
- Redux DevTools integration
- New native stack navigator that uses native navigation primitives for navigation using the react-native-screens library
- New backends for Material top tab navigator based on react-native-viewpager and ScrollView
- Other improvements – Revamped drawer navigator, simpler API for reset action, reliable focus, blur events, InterationManager integration and better handling of safearea.
Installation and Setup
First of all let’s setup react-native app, we will use react-native-cli for creating the application.
|
1 |
npm install -g react-native-cli |
After installing react-native-cli, now create an application using the following command.
|
1 |
react-native init NavigationSampleApp |
Now install the react-navigation library –
|
1 |
npm install @react-navigation/native |
Now install the following dependency libraries for react-navigation –
|
1 |
npm install react-native-reanimated react-native-gesture-handler react-native-screens react-native-safe-area-context @react-native-masked-view/masked-view |
We are done with the installation part now. Let’s set up the folder structure and add components for implementing react-navigation through example.
We will understand all types of navigator with examples individually and then will see an example where all navigators are combined.
Let’s start with different navigators individually.
Stack Navigator
The stack navigator is a stack containing the screens of your app. First screen defined among all screens of stack navigator is the root screen unless we define explicitly initialRouteName to a particular screen. As we move from one screen to another in the stack, the new screen is placed on top of the stack.
Install the react-navigation-stack package –
|
1 |
npm install --save @react-navigation/stack |
Now we will configure the stack navigator in App.js/tsx file as given below.
App.js/tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
import React from 'react'; import { View, Text, StyleSheet, Button } from 'react-native'; import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native'; import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack'; import { HomeScreen } from './HomeScreen'; import { DetailsScreen } from './DetailsScreen'; const Stack = createStackNavigator(); export default function App() { return ( <NavigationContainer> <Stack.Navigator> <Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} options={{ title: 'Home Screen' }} /> <Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} /> </Stack.Navigator> </NavigationContainer> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', }}) ; |
- First of all, import all screens which we want to keep in stack.
- Then we created an instance of createStackNavigator and defined each screen with the help of the instance in the NavigationContainer wrapper. Navigation container maintains the state of routes in our application.
Let’s create our screens
HomeScreen.tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
import React from 'react'; import { View, Button, Text, StyleSheet } from 'react-native'; export function HomeScreen(props: any) { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Button title="Who is Brendon Eich" color= '#800080' onPress={() => { props.navigation.navigate('Details', { details: 'Brendon Eich is an American technologist and creator of the JavaScript programming language.', }); } } /> </View> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', }}) |
Each screen within the stack will carry navigation as props, thus each will have access to Navigation’s navigate() function which enables us to move on another screen.
We have passed two params in the navigate function, first one is ‘Details’ which is the route name of DetailsScreen which we defined in App.js/tsx. The second one is navigation parameter with key ‘details’ and some information is stored in it.
DetailsScreen.tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
import React from 'react'; import { View, Button, Text, StyleSheet } from 'react-native'; export function DetailsScreen({ route, navigation }: any) { const { details } = route.params; return ( <View style={styles.container}> <View style={styles.innerContainer}> <Text style={{ color: '#FFF' }}>{details}</Text> </View> </View> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', }, innerContainer:{ justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#800080' } }) |
- In DetailsScreen, we’re accessing the same route params we passed in from HomeScreen.tsx.
Applying styles to header
Modify App.js/tsx to add header styles –
App.js/tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
import { StatusBar } from 'expo-status-bar'; import React from 'react'; import { View, Text, StyleSheet, Button } from 'react-native'; import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native'; import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack'; import { HomeScreen } from './HomeScreen'; import { DetailsScreen } from './DetailsScreen'; const Stack = createStackNavigator(); export default function App() { return ( <NavigationContainer> <Stack.Navigator screenOptions={{ headerStyle: { backgroundColor: '#800080', }, headerTintColor: '#fff', headerTitleStyle: { fontWeight: 'bold', }, }} > <Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} /> <Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} /> </Stack.Navigator> </NavigationContainer> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', }, }); |
Tab navigator
Tabs can be found in most, if not all, apps today, and so ours should have some too! As with the stack, we’ll need to install this package separately:
|
1 |
npm install @react-navigation/bottom-tabs |
We need icons for our tabs so we are installing react-native-vector-icons.
|
1 |
npm install --save react-native-vector-icons |
Now link your dependencies for icon assets with the command below –
|
1 |
React-native link |
You can use the link below for a complete setup guide –https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-native-vector-icons
Update HomeScreen & DetailsScreen as following as we can not pass params directly between tabs-
HomeScreen.js/tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
... <Button title="Who is Brendon Eich" color= '#800080' onPress={() => { props.navigation.navigate('Details'); } } /> ... |
DetailsScreen.js/tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
... export function DetailsScreen() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text style={{ fontSize: 20 }}>Details Screen</Text> </View> ); } ... |
Modify App.js/tsx
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
import React from 'react'; import { View, Text, StyleSheet, Button } from 'react-native'; import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native'; import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack'; import { createBottomTabNavigator } from '@react-navigation/bottom-tabs'; import { HomeScreen } from './HomeScreen'; import { DetailsScreen } from './DetailsScreen'; import Ionicons from 'react-native-vector-icons/Ionicons'; const Tab = createBottomTabNavigator(); export default function App() { return ( <NavigationContainer> <Tab.Navigator screenOptions={({ route }) => ({ tabBarIcon: ({ focused, color, size }) => { if(focused) color = '#800080' else color = 'gray' let iconName= "Home"; if (route.name === 'Home') { iconName = 'ios-home'; } else if (route.name === 'Details') { iconName = 'ios-list'; } return <Ionicons name={iconName} size={size} color={color} />; } }) } >. <Tab.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} /> <Tab.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} /> </Tab.Navigator> </NavigationContainer> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff', alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center', }, }); |
Conclusion
Being able to configure navigation configurations dynamically is one of the most important features of react navigation 5. And newly added hooks are super helpful in handling navigation events with great efficiency. Overall features introduced in this react-natigation API will help in creating a better navigation experience for users.
All navigators combined code can be found with git repo link given below-
Related content
Auriga: Leveling Up for Enterprise Growth!
Auriga’s journey began in 2010 crafting products for India’s
