Spring Boot with Docker
- General
- DevOps
Spring Boot with Docker
Docker is a tool which is used to automate the deployment of applications in lightweight containers so that applications can work efficiently in different environments.
Common Docker Terms
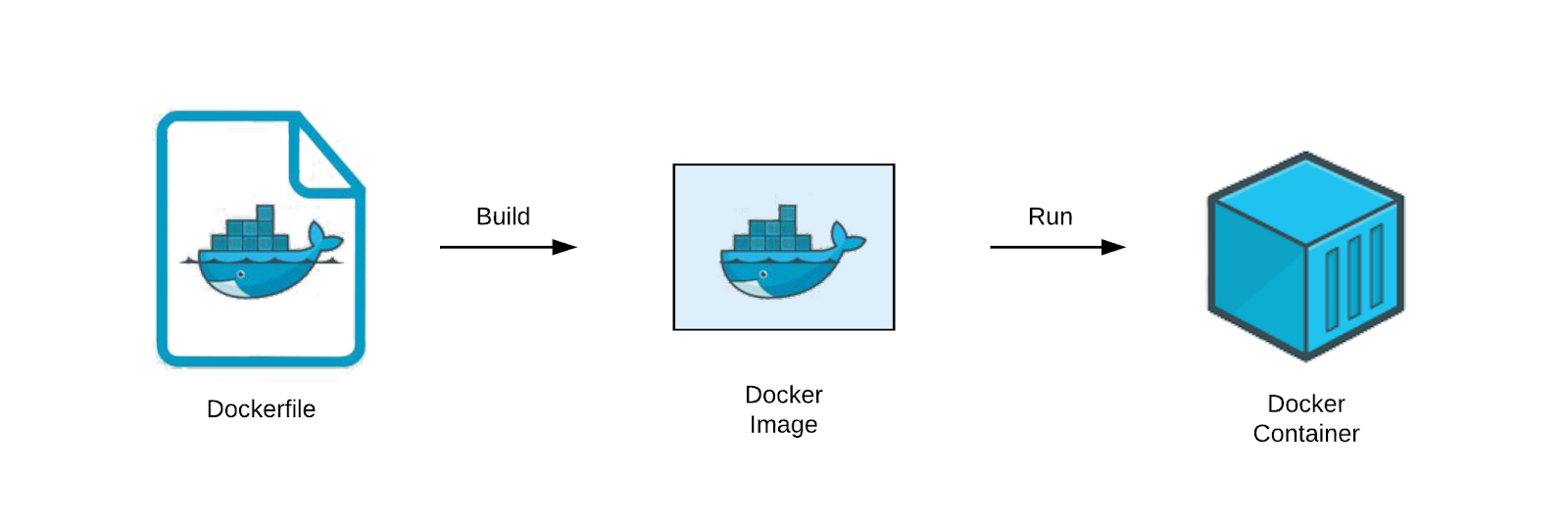
Docker Container
A container is a standard unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies so the application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
Docker Image
A Docker image is a collection of files that bundle together all the essentials, such as installations, application code and dependencies, required to configure a fully operational container environment.
Docker File
A Dockerfile is a script/text configuration file that contains collections of commands and instructions that will be automatically executed in sequence in the docker environment for building a new docker image.This file is written in a popular, human-readable Markup Language called YAML.
Docker Hub
Docker Hub is a service provided by Docker for finding and sharing container images with your team.

Step by step process
Install docker engine
Follow docker official site for installation
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/
Create docker file
Create plain text file in root of the project and named it as Dockerfile
Write this content in the file Dockerfile:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
#openjdk is the base image FROM openjdk:11 # copy jar file into container image under app directory COPY target/*.jar app/app.jar # expose server port accept connections EXPOSE 8080 # start application CMD ["java", "-jar", "app/app.jar"] |
Create project build
Before creating a docker image make sure you have created project build.
If you already created the latest build then you can skip this step.
Create docker image
Use this command for creating docker image:
$ docker build -t username/repository:tag
|
1 |
docker build -t aurigait/spring_docker:new-release . |
– aurigait is the username of your docker hub account
– springDocker is the name of the repository in docker hub (if repository does not exist in docker hub it will automatically created when you push image to docker hub)
– new-release is the tag which is used to differentiate multiple image in same repository
Pushing image to docker hub
- Login with docker hub credential
$ docker login -u username - For pushing image use this command:
$ docker push username/repository:tag
Till this step you have created a docker image which can run on any machine having docker installed.
Running docker image
Before running the image please make sure you have docker installed on your machine.
Use this command:
$ docker run -p [host port]:[container port] username/repository:tag
|
1 |
docker run -p 8080:8080 aurigait/spring_docker:new-release |
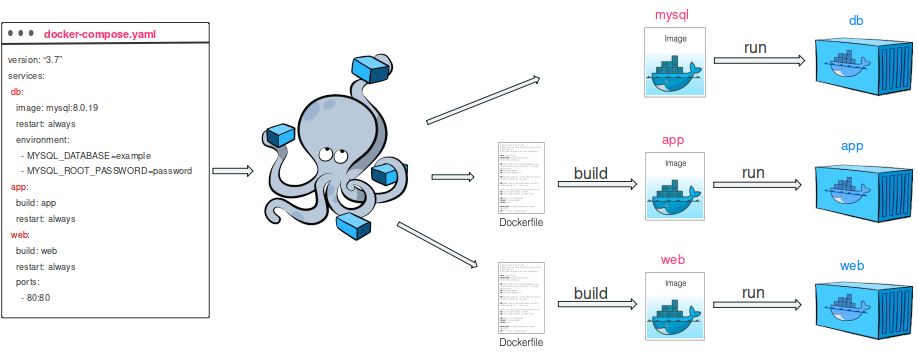
Docker Compose
Docker Compose is used to run multiple containers as a single service. You could create one file which would start multiple containers as a service without the need to start each one separately.
Step by step guide:
1. Install docker compose
Refer official docker document: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
2. Create docker-compose.yml file
A docker-compose.yml is a config file for docker-compose.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
version: '3' services: docker-spring: image: "aurigait/spring_docker/new-release" restart: always ports: - 8080:8080 depends_on: - docker-mysql docker-mysql: image: "mysql" restart: always ports: - "3307:3306" environment: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Karan@123 MYSQL_DATABASE: spring_docker volumes: - ./data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql |
4. Running docker container
For running docker container you need to use following command which will follow the step by step process in docker-compose.yml file and run the container.
|
1 |
docker-compose up |
4. Stopping docker container
For stopping docker container you can follow this command:
|
1 |
docker-compose down |
Related content
Auriga: Leveling Up for Enterprise Growth!
Auriga’s journey began in 2010 crafting products for India’s
